Tips for Growing Flowers in a Greenhouse
Growing flowers in a greenhouse can transform a simple gardening hobby into a flourishing passion. The controlled environment of a greenhouse offers a unique opportunity to cultivate a wide variety of flowers, regardless of the season.
Explore how to grow flowers in a greenhouse, from picking the right types of flowers to managing the perfect amount of light, temperature, and humidity. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a budding enthusiast, the following tips will help you develop your skills, ensuring vibrant blooms and a rewarding gardening experience year-round.
Understand the Basics of Greenhouse Gardening
Understanding greenhouse gardening basics can help you cultivate a thriving flower garden. Greenhouses come in various types, from basic lean-to designs to elaborate gabled structures, each requiring a strategic setup for optimal growth.
The ideal location is a level, well-draining site with maximum sunlight exposure, preferably facing southwards to maximize direct sunlight while avoiding shaded areas.
You also need proper ventilation, so ensure you maintain enough space around the greenhouse for air circulation and easy access to power and water sources for utilities like heating, cooling, and irrigation systems. For the best growth conditions, ensure that your greenhouse has:
-
Daytime temperatures generally ranging from 65 to 75°F
-
Nighttime temperatures around 55 to 65°F
-
Constant moderate airflow for adequate ventilation
-
A soil pH between 6.2 to 6.8
-
Ample bright light from natural sun exposure and supplemental LED grow lights
Prepare Your Greenhouse for Flower Planting
Disease from previous crops can quickly destroy young seedlings, while a damaged or dirty greenhouse can negatively impact light penetration and diffusion, and temperature control. Before you sow or start flower seeds in your greenhouse, take the following steps:
Sanitize the Greenhouse
Before you bring any plants into your greenhouse, clean it thoroughly to create a healthy environment for growth. Disinfect everything, including shelves, benches, and tools, to avoid diseases, pests, or weeds from past plants. You can use a white vinegar or 10% bleach solution for cleaning.
Also, remove old plant leftovers and dust to make your greenhouse a clean, disease-free space.
Select the Right Soil Mix and Pots
Choose a high-quality, sterile potting mix for flowers and vegetables for successful greenhouse flower planting. This mix should ideally contain peat, perlite, and vermiculite, ensuring a lightweight, moisture-retentive, and well-draining growth medium.
Select pots based on your flowers’ needs: porous clay pots for plants requiring dry conditions, moisture-retaining plastic pots for most flowers, or ceramic pots with drainage holes to prevent root rot.
Match the pot size to the plant’s mature size. Small flowers like marigolds thrive in 8” to 12” pots, while larger blooms like dahlias need 12” to 18” inch pots for optimal root growth and overall health.
Set Up an Irrigation System
Consider setting up a drip irrigation system with a timer to make watering your greenhouse flowers easier and more effective. This automated approach delivers water directly to the base of each plant, providing consistent and accurate watering while reducing water waste. For smaller greenhouses, a simple watering can is ideal. Just ensure that you’re watering evenly and thoroughly.
Whether you choose an automated system or manual watering, the key is to maintain steady moisture levels. Proper irrigation is essential for keeping your greenhouse flowers healthy and thriving, ensuring they get just the right amount of water without increasing greenhouse humidity or causing infections like downy mildew or botrytis blight.
Selecting the Right Flowers for Greenhouse Farming
Greenhouse flowers grow best in certain seasons when your greenhouse is kept at specific temperatures, humidity, and light levels. Below is a table that outlines the growing conditions for various popular greenhouse flowers. These conditions can vary based on specific cultivars and regional differences.
| Flower Type | Ideal Temperature (°F) | Season for Growth | Ideal Humidity (%) | Light Level |
| Roses | 60 - 75 | Year-round | 60 - 70 | Bright, indirect |
| Orchids | 65 - 80 | Year-round | 40 - 70 | Moderate, indirect |
| Geraniums | 65 - 75 | Spring - Fall | 50 - 60 | Bright, direct |
| Chrysanthemums | 60 - 70 | Fall | 50 - 60 | Bright, indirect |
| Begonias | 65 - 75 | Spring - Fall | 50 - 60 | Moderate, indirect |
| African Violets | 65 - 75 | Year-round | 40 - 60 | Moderate, indirect |
| Petunias | 60 - 70 | Spring - Fall | 40 - 50 | Bright, direct |
| Lilies | 60 - 65 | Spring - Summer | 50 - 60 | Bright, indirect |
| Cyclamens | 50 - 60 | Winter | 50 - 60 | Moderate, indirect |
Planting and Nurturing Flowers in a Greenhouse
Cultivating greenhouse flowers is about more than just managing humidity, temperatures, and light. You need to know how, when, and where to plant your flowers in your greenhouse to foster maximum growth.
When and How to Plant Your Flowers
It’s best to sow seeds directly into pots or planting beds for annuals and vegetables. Follow the seed packet’s recommended sowing schedule to ensure optimal germination. Typically, this involves planting in late winter or early spring for summer blooms or in the fall for spring flowering.
When it comes to perennials, start with young plants purchased from nurseries. Transplant these into your greenhouse beds, timing it according to each plant’s specific needs. For instance, summer-flowering perennials like echinacea and rudbeckia should be transplanted in early spring, whereas spring peonies and irises are best transplanted in the fall.
After planting, water the seeds or young plants gently. This helps avoid disturbing the roots. Ensure they receive adequate light and warmth, which are crucial for germination and early growth stages.
Spacing for Proper Growth
Proper spacing between flowers is essential for healthy development. Overcrowding can lead to poor air circulation, increased humidity, and a higher risk of diseases. Consult the recommended spacing guidelines for each flower variety, considering its mature size.
Wider spacing allows for improved air circulation and prevents competition for resources, ensuring each flower receives adequate light, water, and nutrients.
Watering and Feeding Your Flowers
Establish a consistent watering and feeding schedule to nurture your greenhouse flowers. Monitor the moisture levels in the soil using a digital moisture meter for the most accurate results, and water when the top few inches become dry. Following package directions, apply a balanced flower fertilizer to promote all-round growth and vibrant blooms.
Consider using slow-release feeds for a more extended and consistent nutrient supply, supporting the flowers throughout their growth stages. A well-hydrated and properly nourished plant is more resilient to pests and diseases, contributing to the overall success of greenhouse flower cultivation.
Maintain Ideal Greenhouse Conditions
Your greenhouse helps maintain a controlled environment for your flowers, regardless of season or weather. This stability helps your flowers maximize their growth and yield.
You need to manage several critical greenhouse elements to create the ideal climate for cultivating hot house flowers.
Temperature Control
Ensure stability by actively monitoring greenhouse temperatures using a thermometer. Ventilate on hot days by opening vents, doors, and running fans. Use shade paints or screens in intense sunlight and invest in heating systems for precise temperature regulation, especially during extreme cold.
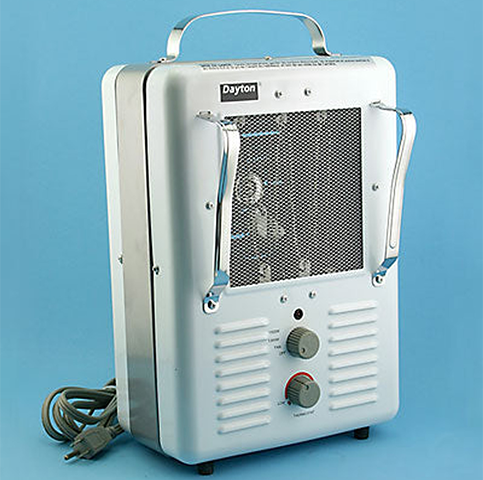

The Dayton 120-Volt Portable Heater provides precise temperature management. This electric heater, with a powerful 5,120 BTU output, includes a selector switch for variable wattage, a fan-only option, and safety features like a tip-over disconnect switch and overheating shutoff.
Humidity and Ventilation
Actively managing humidity and ventilation prevents mold and promotes healthy plant growth. Use automatic ventilation systems and humidity monitors for a simple way to maintain optimal conditions.
Ensure the internal humidity range is between 40-60%, depending on your flower species’ needs, and use dehumidifiers to restore balance in excessively humid conditions.
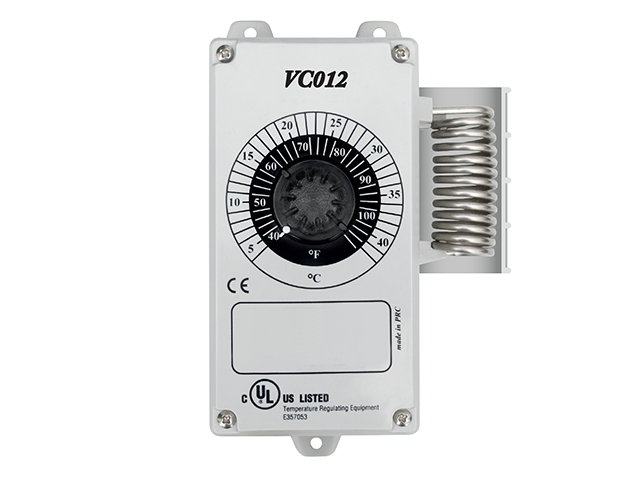

Achieve efficient humidity and ventilation control with Charley’s Greenhouse Thermostat. This quality thermostat automatically regulates fan systems or heaters, featuring a moisture-resistant case and an accurate external stainless steel temperature sensor for swift responses to temperature changes.
Light Control
Supplement natural sunlight with LED grow lights, especially during winter. Maximize natural light through proper glazing and annually cleaning dusty panels. Manage intense summer sunlight with sheets or shade cloths to provide a protective shield without compromising overall flower health.
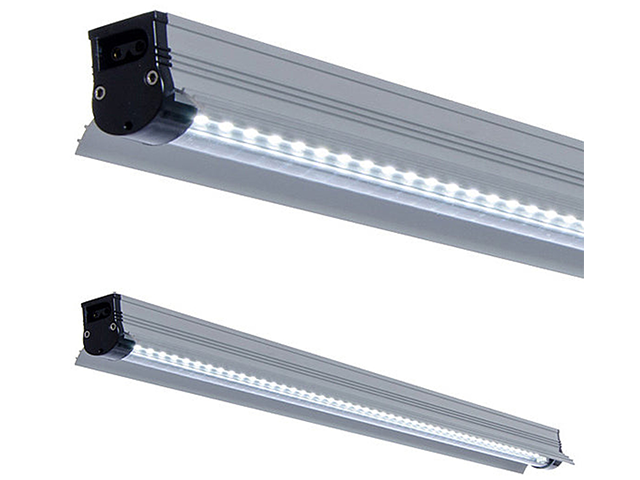

Get optimal lighting inside your greenhouse with Sunblaster LED Grow Light. This high-output strip light, featuring a full spectrum (6400K), efficiently nurtures seedlings. Its self-ballasted design and wide light distribution make it perfect for enhancing natural light on cloudy days.
Common Pests and Diseases in Greenhouse Flowers
Warm and humid conditions, which allow greenhouse flowers to flourish, also create an environment that encourages pests and diseases. To effectively tackle these issues, follow these simple steps:
Identifying Common Pests and Diseases
Keep a close eye on your greenhouse plants for potential threats like aphids, whiteflies, spider mites, thrips, scale, caterpillars, and fungus gnats. Detecting these pests early is vital for effective management.
Also, check for fungal problems, such as powdery mildew, grey mold, and blights, which can spread rapidly in the moist greenhouse environment.
Pest Control and Disease Prevention
Implement control strategies such as maintaining proper temperatures, spacing plants adequately, and ensuring sanitation to prevent issues. Remove and dispose of diseased plants quickly to curb the spread of diseases like powdery mildew and root rot.
When you spot pests, act promptly by using fly traps, neem oil, or introducing predatory insects. Avoid using chemical pesticides that can harm beneficial insects. Instead, choose neem oil as an organic insecticide and fungicide or bring in natural predators like ladybugs and lacewings to safely eliminate pests.
For preventive measures, use organic fungicides like sulfur and copper. To eliminate disease spores, keep things clean by sterilizing tools and greenhouse surfaces with hydrogen peroxide or a bleach solution.

Discover the effectiveness of our organic pest management solution, the 70% Neem Oil. This 1-pint concentrate serves as an insecticide, miticide, and fungicide, efficiently controlling pests and diseases to preserve the health of your greenhouse plants naturally.
Combat pests in an eco-friendly way with our Solar Yard Gard Pest Repeller. This solar-powered solution is effective against deer, squirrels, and rabbits. Adjustable frequencies provide a humane and environmentally friendly method to safeguard your greenhouse, covering up to 3,000 sq. ft.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Care of Greenhouse Flowers
Typically, flowers are best harvested in the cool, early morning hours when they’re fully hydrated. The exact timing varies by species, but a common sign that your flowers are ready for harvest is when the first few buds begin to open. Use clean, sharp tools, like floral shears, to cut the stems at an angle; the increased surface areas will help them absorb water more efficiently.
Immediately after cutting, place the stems in a clean container with water and a floral preservative. You can make your own floral preservative by adding 2 tablespoons of sugar and 2 tablespoons of white vinegar or lemon juice to a quart of water and stirring until dissolved. This mixture nourishes the flowers and inhibits bacterial growth. Keep them in a cool, shaded area for a few hours to let them hydrate before arranging or packaging.
Maintain a cool, humid environment for storage, typically between 33°F to 35°F. This slows down their metabolism and extends their shelf life. Avoid storing flowers with fruits, as fruits emit ethylene gas that can accelerate flower aging. Change the water every 2 to 3 days, and trim ½” off the stems at a 45° angle to ensure the flowers stay fresh longer.
Discover the Benefits of Greenhouse Flower Gardening
Growing flowers in your greenhouse can ensure a year-round supply of fresh blooms for your home. However, learning how to increase your yield and extend the lifespan of your flowers will enable you to fully benefit from your greenhouse.
Optimize your greenhouse growing strategies with high-quality equipment from Charley’s Greenhouse & Garden. Explore our complete range to create the ideal growing environment for your hot house flower garden.


